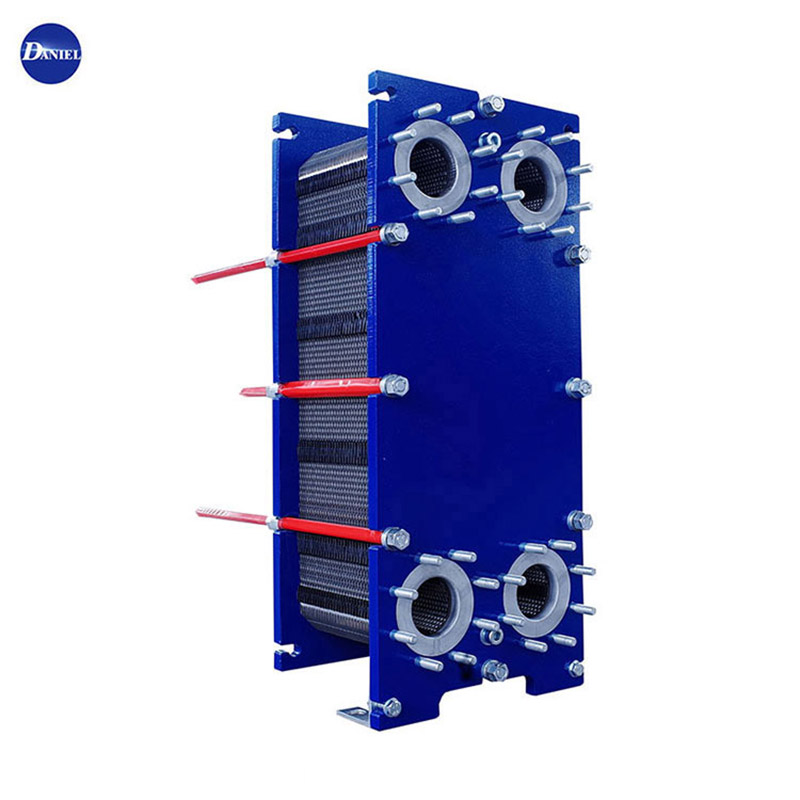
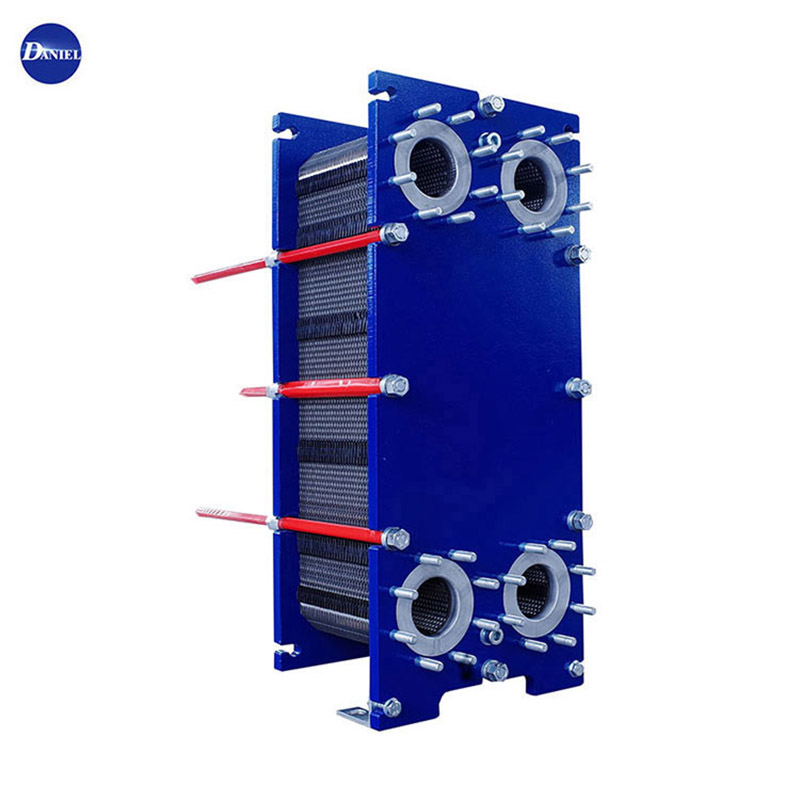
Heat Exchanger Plate
A heat exchanger plate refers to the individual plate component used in a plate heat exchanger. It is a thin, flat, and typically corrugated metal plate that plays a crucial role in facilitating heat transfer between two fluid streams in a plate heat exchanger.Here are some key features and characte......
Send Inquiry
Product Description
A heat exchanger plate refers to the individual plate component used in a plate heat exchanger. It is a thin, flat, and typically corrugated metal plate that plays a crucial role in facilitating heat transfer between two fluid streams in a plate heat exchanger.
Here are some key features and characteristics of heat exchanger plates:
1. Material: Heat exchanger plates are usually made of metals such as stainless steel, titanium, or nickel alloys. The choice of material depends on factors such as the operating temperature, corrosion resistance requirements, and specific application.
2. Corrugations: Heat exchanger plates have corrugations or ridges on their surfaces. These corrugations increase the heat transfer area and promote fluid turbulence, enhancing the efficiency of heat transfer between the fluids.
3. Gasket Grooves: Heat exchanger plates typically have grooves along their edges or surfaces to accommodate gaskets. The gaskets create a sealed flow path for the fluids and prevent mixing between the two streams.
4. Flow Channels: Heat exchanger plates have fluid channels or passages formed by the corrugations. These channels alternate between the hot and cold fluids, allowing for efficient heat exchange. The arrangement and pattern of the channels can vary based on the specific design and application of the plate heat exchanger.
5. Thickness: The thickness of heat exchanger plates can vary depending on the design, application, and required structural strength. Thinner plates provide higher heat transfer rates but may be more susceptible to damage, while thicker plates offer better durability but may have slightly reduced heat transfer efficiency.
Heat exchanger plates are arranged in a stack within the plate heat exchanger. The fluid streams flow through the channels between the plates, with one fluid passing on one side of the plate while the other fluid flows on the other side. The corrugated surface of the plates promotes turbulence and maximizes the contact between the fluids, facilitating efficient heat transfer.
The design and configuration of heat exchanger plates may vary based on the specific requirements of the heat exchanger, including the desired heat transfer capacity, pressure drop limitations, and fluid properties. The plates can be easily removed and replaced for cleaning or maintenance purposes, allowing for easy inspection and maintenance of the heat exchanger.